NPM
Exploring npm Package Vulnerabilities and Effective Auditing
This article part of a series on Mastering npm in the Enterprise, also available as a chapter in our free, downloadable eBook
Seen scary vulnerability alerts when you’re coding with npm packages? Worried about the security of your JavaScript apps due to the latest exploit scare; like when several widely used JavaScript libraries were compromised? When you build JavaScript apps, you often use npm packages for managing libraries. Keeping these packages safe for production is super important.
When building JavaScript apps, you often rely on npm packages to manage libraries—but these packages aren’t always safe. Vulnerabilities, poor-quality code, or even malicious updates can put your applications at risk. In one well-known incident, several widely used JavaScript libraries were compromised with code intended to steal cryptocurrency. Keeping your packages audited and secure is essential to protect your apps in production.
I’m guessing you probably run npm audit to check your packages, right? Auditing your npm packages, you’ll find lots of security warnings. It makes you wonder: How do you fix them? Are “Low severity” warnings no big deal? And what about the scary “High severity” ones? How do they affect my code? Do I even need to do anything about them?
It’s a lot to digest. In this article, we’ll take a look at npm package vulnerabilities and the auditing process, as well as the challenges you have to deal with. I’ll also talk about what you should understand to make informed decisions and how to sort out your vulnerabilities.
Understanding npm Package Vulnerabilities and Auditing
npm vulnerabilities are security weaknesses identified in JavaScript packages and reported to a central database. For example, the “jQuery” package has a vulnerability related to “Object.prototype pollution”:
These kinds of vulnerabilities pose potential security risks. Running npm audit gives you a list of vulnerabilities and the affected package versions, but it only gives you an overall severity rating for your package dependency, using the highest returned severity. (“critical”, “high”, etc… ) This makes it hard to figure out which vulnerabilities need your immediate attention.

Keep in mind, an audit only compares your npm packages against a database of reported vulnerabilities. Bottom line is, it’s not a comprehensive virus scan, nor does it eliminate all vulnerabilities. What’s more, it scans only one database (GitHub Advisory Database), so vulnerabilities reported elsewhere will not be detected.
In any case, it’s a big step toward improving security. However, the “severity” of these vulnerabilities shouldn’t influence your response. For example, even though the “jQuery” vulnerability we looked at has a “Moderate” severity rating, there’s not much risk to using it.
Now, imagine someone injecting a crafted payload, potentially manipulating the Object.prototype and compromising your application’s integrity. For an application protected behind your firewall, you won’t need to worry too much. The severity rating doesn’t account for the likelihood of exploitation or the impact on your application.
Most vulnerabilities are not easily exploitable. If they need particular access rights or aren’t accessible through regular user interactions, the risk of exploitation is trivial. It’s important to assess the context when deciding how to address vulnerabilities, especially when the audit gives you an overall severity rating without individual details.
So, How Can We Handle Vulnerabilities?
First and foremost, avoid just blindly upgrading your packages. Instead, consider:
✔ Regularly monitoring packages used in production for updates
✔ Routinely checking security advisories like GitHub Advisory Database (GHSA) and NVD
✔ Employing automated scanning tools to identify new vulnerabilities
✔ Evaluating vulnerabilities based on actual risk rather than solely on severity
It’s all about that zen balance. Mindlessly upgrading whenever new updates are available isn’t the best move, as not all detected vulnerabilities pose a threat to your code. One thing they could do though is introduce unknown vulnerabilities or screw with your application.
Case in point, if you were to blindly upgrade “jQuery” to the latest version, you might encounter production errors because of changes in object deserialization.
What’s more, you can’t just rely on the npm client’s built-in auditing. You’re not getting guidance on how to resolve detected vulnerabilities. The implied advice is, you guessed it —just to upgrade. Again, this might do more harm than good.
Evaluate Vulnerabilities Case by Case
Instead of always going down the upgrade route, start by determining if a vulnerability needs mitigation or can be safely ignored. The reported vulnerability may not have much of an impact on your application.
Will there be a realistic opportunity for a malicious actor to inject a crafted payload and exploit Object.prototype? What are the potential consequences of a Denial-of-Service attack on our application?
While the built-in npm vulnerability auditing feature is valuable, it shouldn’t be your only source of information. Combine data from different sources and conduct independent assessments of each package.
Maintain Consistency in Your Assessments
When you think about it, an “assessment” is basically someone’s subjective judgment of a vulnerability’s severity at a given time. But what one person considers “critical,” another may not regard it as serious. Even if one person conducts multiple scans, evolving threats or increased knowledge can alter their judgment over time.
If you’re going to assess your vulnerabilities efficiently, you’re going to have to figure out how to keep things consistent.

Should I Just Skip Vulnerability Scanning Altogether?
Assessing vulnerabilities in npm packages can be time-consuming and labor-intensive. You have to systematically review each vulnerability, research potential risks, and determine appropriate responses. Added to that, you must communicate this information to your team (or your future self) to avoid repetitive work when similar vulnerabilities crop up in the future. This is going to lead to review fatigue, leading to overlooking vulnerabilities that need a more thorough assessment.
So, should you skip vulnerability scanning entirely?
No! You should still audit your packages and evaluate reported vulnerabilities on a case-by-case basis. While most vulnerabilities may pose no real threat, do you really want to risk a problematic package slipping through the cracks? Thankfully, automated scanning tools can simplify this process significantly!
How Scanning Tools Can Enhance Your Vulnerability Assessments
Automated scanning tools, such as ProGet can greatly enhance the efficiency of your vulnerability management:
⚙ Assessment management allows you to configure different types of assessments (block, ignore, caution, etc.) and document comments, ensuring that everyone can follow and understand the decisions made.

⚙ Automated vulnerability assessment allows you to establish rules based on the reported severity (low, medium, critical, etc.), reducing the need for immediate reactions to new vulnerabilities. You can later apply judgment and modify the auto-assessment as needed.
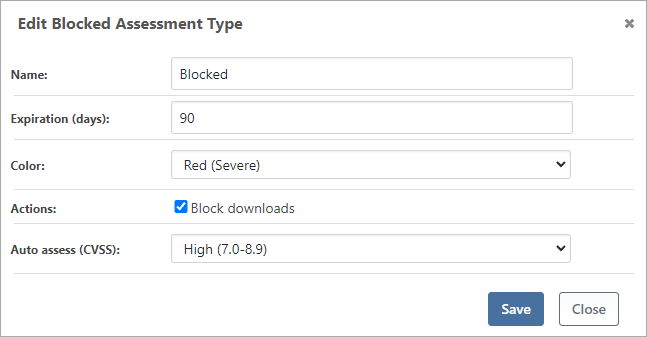
⚙ Download blocking can enforce the use of approved packages only, minimizing potential vulnerabilities and clearly communicating this requirement to developers. Attempting to download unapproved packages would result in errors.

⚙ Integrated native npm audit support uses ProGet’s vulnerabilities and assessments removing the need for developers to have to handle this themselves, making things even more efficient!

Now running npm audit will also link users to details of the vulnerability in your own ProGet instance, allowing you to leave comments regarding the vulnerability for your team to see.

Additionally, ProGet is bundled with the “ProGet Vulnerability Center” (PGVC), an up-to-date aggregation of prominent vulnerability databases, including the GitHub Advisory Database (GHSA) and the Global Vulnerability Database. You no longer need to continuously monitor various vulnerability databases, as all the data is conveniently consolidated.
Take Control of Your npm Vulnerability Management
Vulnerabilities shouldn’t be a significant concern for your applications as long as you take the following steps:
💡 Learn to assess vulnerabilities based on their potential risk and impact, not just their severity.
💡 Make informed decisions regarding how to address identified vulnerabilities.
This means evaluating individual packages instead of blindly upgrading. ProGet can help you maintain consistent and reliable vulnerability assessments by providing automated assessments against a consolidated, offline vulnerability database.
That was quite a bit to cover, and I’d suggest keeping a handy summary of it for future use. Why not sign up for our guide, Mastering npm in the Enterprise. It includes more on managing vulnerabilities, as well as managing packages and optimizing workflows in your organization, and much more. Sign up for our free copy today!
